Table of Contents
- See Also
- python.forDSM
Aim of script
calculates a raster DSM from point cloud data, optimized for forested areas.
General description
The python script forDSM implements the DSM derivation approach of Hollaus et al, 2010, referred to as "land cover dependent DSM". The surface model is calculated as a combination of a raster containing the highest data point within each cell (DSMmax) and a grid obtained from moving least squares interpolation (DSMmls) with a tilted plane as base model (i.e. moving planes interpolation). The moving planes interpolation has the following advantages compared to the mere rasterization of the DSMmax model: (i) a more flexible point neighbourhood is considered by extending the selection area beyond the domain of the grid cell, and (ii) the sigma0 of least squared interpolation provide a roughness measure. The latter is calculated from the residuals of the plane adjustment (deviation between the heights of the data points and the heights of the best fitting plane at the x/y locations of the data points). High roughness values are hereby used as an indicator of vegetation areas and/or immediate height jumps in the terrain (e.g. at roof boundaries) as the points from both the ground and the canopy (or roof, power line...) are used in the plane interpolation. In these areas the DSMmax is used in the final DSM to to avoid underestimation of the canopy heights. Small roughness values, in turn, indicate smooth surfaces like bare ground or roofs. In this case the smoother DMSmls is preferred to avoid artificial height jumps in the final product. More details about the approach can be found in Hollaus et al, 2010.
Basic algorithm
The algorithm consists the following steps:
- Raster based homogenization of the data distribution using Module Cell , by selecting the highest points within a relatively fine raster (i.e. ca. half of final grid size of the target DSM). Although the processing is raster based, the outcome of this steps is a subset of the original data points which are stored in an OPALS Datamanager (ODM) file. This odm-file is used as input for the following two processing steps.
- Calculation of DSMmax raster model extracting the highest elevations within each raster cell from the ODM using Module Cell . If no data points are availabe in a cell, the respective cell is marked as a void (no data).
- Calculation of DSMmls grid model using Module Grid . For each grid point the height is interpolated by estimating a best fitting tilted plane based on the k-nearest data points in a maximum search radius around the grid point. In addition to the grid heights, a roughness measure (standard deviation σ0 of the plane adjustment) is estimated and stored in a separate raster.
- Calculation if the final land cover dependent DSM by merging DSMmax and DSMmls based on the σ0 roughness layer using Module Algebra . DSMmax is used in rough areas (i.e. σ0 greater than a specified threshold) and DSMmls otherwise. In addition, data voids in the DSMmax model are filled with DSMmls values.
Usage of script
The input (-i, –input) can either be a single ODM file or a list of ODM files (e.g. an entire directory containing multiple ODMs). In case multiple ODMs are specified, the ODMs should not contain redundant data as proper data overlaps are for avoiding border discontinuities are considered by the script internally. This especially applies to large, tiled datasets (e.g. entire flight blocks, project areas, or even country-wide data) which should be provided without overlap. All temporary products (intermediate ODMs and rasters) are stored in a folder which can be specified with opalsparam{-t, –temp}. The output folder for storage of the final DSMs is specified by -o, –output. By default, a single land cover dependent DSM is calculated from the entire area of all input data set. However, a user defined limit window (xmin ymin xmax ymax) can be specified via -l, –limits and tile based processing is enabled, when either specifying a tile size (-t, –tileSize) or by providing a shape file containing a set of (rectangular) polygons. In case of tile based DSM creation a comprehensive DMS mosaic can be generated by setting parameter -m, –mosaic to "1".
Please note, that all specified paths are interpreted relative to the project directory (-p, –projectDir) unless absolute paths are provided. Already existing temporary products are either calculated anew or re-calculation is skipped depending on the state of parameter -x, –skipIfExists.
Parameter description
Remark :Optional, default: '*'
Description:
Remark :Optional, default: '.'
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional, default: 'E:\autobuild\swdvlp64\opals\TEMP'
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional
Description:
Remark :Optional, default: 0
Description:
Examples
The data used in the following examples can be found in the $OPALS_ROOT/demo/ directory.
As a prerequisite for the subsequent examples, please import the data using the following commands:
Example 1
This example generates a simple, tiled DSM, and additionally a mosaic:
Example 2
When using a shapefile as argument for the –tileSize parameter, a separate DSM is created for each polygon of the shapefile. –attribute sets the output filenames to be determined by the "polygon_id"-Attribute in the shapefile. –binarymap 1 will create an additional tif-File with the binary map.
Example 3
This example shows how to override settings made in the configuration file (.cfg). For the grid calculations, 8 neighbours and a search radius of 10 m are used. The output cell size will be 0.2 meters. Since tiling is not activated, the output will be a single raster file in GeoTiff format.
Example 4
The Python script forDSM.py can take and process multiple input files at once. The following example shows two different ways to do so, using the strip*.laz files of the same flight block.
In the first case, all of the files are chosen using the wildcard character (*), while in the second case only specific files are selected using the semicolon (;) as separator. In the figure that follows, the derived 0.1m DSM grid is shown (using all strips).
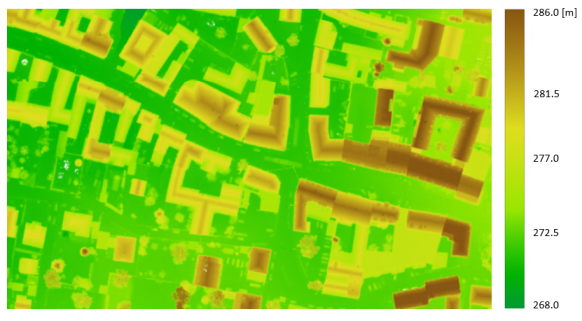
Example 5
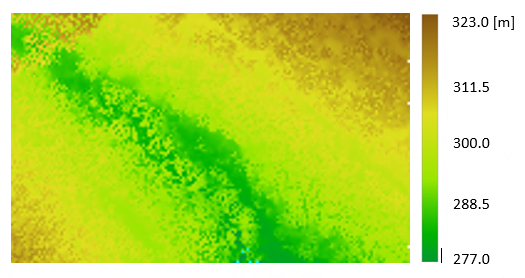
This example gives some guidance on how to use the limit window (-l,--limits) in order to select a subset of the entire area. Here, the full-waveform file fullwave.fwf is used.
The resulting 0.8m DSM is illustrated in Figure 2:
Example 6
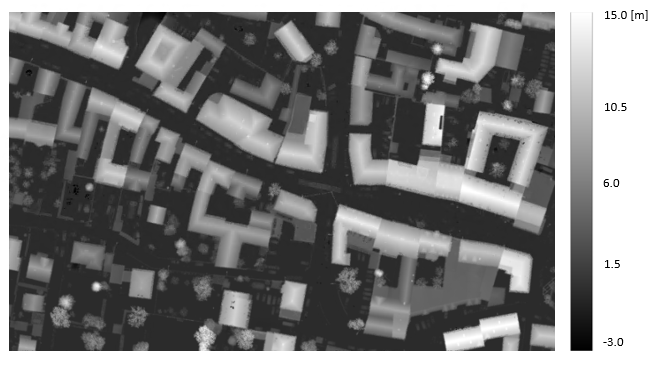
A way to facilitate the interpretation of a DSM is to derive the normalized DSM (nDSM). A nDSM is the difference model "DSM minus DTM" and, therefore, represents heights above the terrain. In this example, it is shown how to create the nDSM, when the DTM is provided. The DSM is derived again from the six .laz files used previously in Example 4 and the DTM is already provided in the $OPALS_ROOT/demo/ directory.
The resulting nDSM (Fig.3) has gridsize of 0.1 meters and it was calculated using the module opalsAlgebra.
References
Hollaus, M., Mandlburger, G., Pfeifer, N., Mücke, W., 2010. Land cover dependent derivation of digital surface models from airborne laser scanning data, PCV 2010, Paris; in: "IAPRS Volume XXXVIII Part 3A", ISSN: 1682-1750; 221
