Table of Contents
This document describes how to install OPALS on your machine. The first step is to download the latest OPALS release.
Introduction
OPALS is a modular program system consisting of small components (modules) grouped together in packages. As a basic concept, OPALS modules are accessible in three different ways as:
- Command line executables,
- Python modules
- C++ classes (via DLL API)
The general installation of OPALS on Windows and Linux/Unix is described in section Installing OPALS on Windows and Installing OPALS on Unix, respectively. If you are upgrading to a new version, consider a look at the Release notes.
Embedding OPALS modules as C++ classes requires a C++ compiler installation, which is not described in this manual. The structure and contents of an OPALS distribution are explained in section OPALS directory structure.
Installing OPALS on Windows
To install a full-featured version OPALS on MS Windows operating systems, perform the following installation steps:
- Download the OPALS setup and run the executable .
- Select the desired install options as well as the installation directory (referred as
$OPALS_ROOTin the following). - Copy your keyfile (opals.key) to
$OPALS_ROOT/cfg/or$OPALS_ROOT/licence/. - Please not that administrative permissions are required to run the setup program.
IMPORTANT NOTES FOR INSTALLATION ON WINDOWS 7/8/10:
The default program folder is read only to standard users, which has two implications if OPALS is installed there:
- PyScripter needs to be started as administrator since it requires write access to its install folder
- Alternative solution: use the full featured IDE PyCharm instead
- Alternative solution: use the full featured IDE PyCharm instead
- Documentation examples are run from the
$OPALS_ROOT/demo/directory and, therefore, will not work if the opalsShell is started as standard user.- Alternative solution: the setup provides an extra demo data option that copies the demo data to an additional folder that is writable for all users. The standard public windows folder (see environment variable $PUBLIC) is suggested, but a different location can be selected during setup. When ever the documentation refers to the
$OPALS_ROOT/demo/folder (e.g. in the module example section), one should switch to this additional demo folder. For convenience reasons, the OPALS Shell shortcut directly starts up in this additional demo folder.
- Alternative solution: the setup provides an extra demo data option that copies the demo data to an additional folder that is writable for all users. The standard public windows folder (see environment variable $PUBLIC) is suggested, but a different location can be selected during setup. When ever the documentation refers to the
Some OPALS modules (e.g. opalsView, opalsICP and opalsStripAdjust) require the MATLAB Compiler Runtime as a prerequisite. Therefore, the setup program checks if MATLAB or the corresponding Compiler Runtime (CRT) are installed. If not installed, an additional install option is available for download and installation of the corresponding Compiler Runtime from the MATLAB website.
Although OPALS comes with a setup program, it is designed as portable software. The setup doesn't change or add any environment variables, however, an uninstaller entry is added to the Windows registry. Using the OPALS shell ($OPALS_ROOT/opalsShell.bat), all necessary environment variables (PATH, PYTHONPATH...) are set for the current command line session only.
An OPALS distribution contains a fully configured Python installation. For using OPALS with an external python installation see Configuring an external Python installation for details.
Unattended installation on Windows
The OPALS installer also support a silent setup mode for unattended installation. Details on supported command line options can be viewed by starting the setup program with the command line parameter /? or /h.
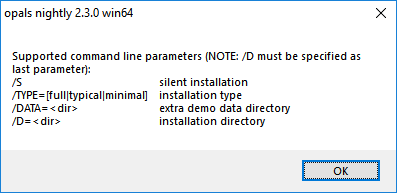
E.g., the following command performs a silent installation of all components to directory C:\opals_2.3.2
Please note that the installation directory (parameter /D) has to be specified as the last parameter. The setup additionally creates an installation log (see $OPALS_ROOT/install.log) which allows to analyse potential installation problems.
Installation on Windows without administrator privileges
In general it is recommended to install OPALS using the provided setup routine. For a low-level installation of the portable OPALS software, the following steps are required:
- Open the setup program program, which is basically a zip archive, with 7-Zip.
- Extract the contained self extracting 7-zip archives (i.e. exe files) into a temporary directory.
- Extract all relevant archives into the desired installation folder (referred as
$OPALS_ROOTin the following). - Make sure that opals users have write permissions to this directory.
- Copy your keyfile (opals.key) to
$OPALS_ROOT/cfg/
OPALS requires following prerequisites to run correctly:
- Installation of Microsoft Visual C++ 2008, 2010, and 2015 redistributable packages. If necessary run the following setup programs:
$OPALS_ROOT/addons/vcredist/2008/vcredist_x64.exeand
$OPALS_ROOT/addons/vcredist/2010/vcredist_x64.exeand
$OPALS_ROOT/addons/vcredist/2015/vc_redist.x64.exe - Some OPALS modules depend on the MATLAB Compiler Runtime (MCR) which is NOT included in the OPALS distribution. See here for further details.
OPALS provides a pre-configured OPALS shell ($OPALS_ROOT/opalsShell.bat), where the internal Python interpreter is configured and all necessary environment variables (PATH, PYTHONPATH...) are set. Thus, no further installation steps are necessary. The shell additionally offers aliases for the command line version of the OPALS modules (cf here).
Advanced Python installation on Windows
For instructions on how to install additional Python packages to the Python distribution that comes with OPALS (internal Python), see section Extending the internal Python installation.
For instructions on how to use an existing Python installation (external Python) in combination with OPALS, see section Configuring an external Python installation.
More information about running OPALS in a Python environment can be found in sections Using OPALS in a Scripting Environment and Using Python Bindings.
Installing OPALS on Unix
This section contains information on how to install OPALS on recent 64-bit Ubuntu systems (14.04 LTS, 16.04 LTS, 18.04 LTS). Other Linux/Unix distributions have not been tested so far. The binary Linux/Unix distribution is provided as a .tar.gz archive, with Python as an external dependency. To ensure/install Python (Version 2.7), enter
in the terminal.
To unpack the archive, execute the following command:
This will create a new folder in your current working directory called "opals_2.3.2". To start the interactive OPALS shell (a special instance of bash), use the following commands
Within this shell environment, you can use the modules of OPALS as on Windows. However, Module names are case sensitive, e.g. opalsAddInfo can be abbreviated as AddInfo, but NOT as addinfo. The OPALS shell also sets up the $PYTHONPATH environment variable for use of the OPALS modules within Python scripts or a shells.
Please note that the opalsShell does not source your ~/.bashrc file by default, since functionality cannot be guaranteed. Experienced users, being aware of the implications, might want to source it themselves (add source ~/.bashrc to the end of opals.bashrc)
Further optional install steps:
- install the Matlab runtime to enable MATLAB dependent OPALS modules (Module View, Module ICP and Module StripAdjust)
- for a fully featured Python IDE download the separate PyCharm archive . Necessary setup steps and further details on PyCharm can be found in the PyCharm section.
- if you consider to use the tree based classification, the R AddOn needs to be installed.
OPALS bash scripts on Linux/Unix
The opalsShell is set up to be used as an interactive command line as well as an interpreter for bash (.sh) script files. You can create executable OPALS script files by putting a shebang at the first line of your script.
By changing the path to the opalsShell script in the shebang, you can have a script choose one of multiple OPALS installations. If you set the executable bit chmod +x script.sh, you can run the script with ./script.sh or by double-clicking on it in a file manager. It will get executed in the correct environment.
Finally, OPALS for Linux/Unix is still work in progress with some restrictions compared to the Windows version. If you encounter problems, please send your bug report to the OPALS developer team
Matlab runtime
Some OPALS modules require the MATLAB Compiler Runtime to be installed (not needed if the correct version of MATLAB is installed). The OPALS setup for Windows installs the runtime automatically, by downloading the correct package from the MathWorks homepage. If necessary, the runtime can be downloaded and installed manually, as required for Linux/Unix. Currently, OPALS depend on version R2017b (9.3).
Important note for Linux/Unix: Currently it is necessary to install the MATLAB Compiler Runtime to the default folder (/usr/local/MATLAB/MATLAB_Runtime) otherwise the OPALS modules will not find the Runtime.
R AddOn
The tree based classification method requires an R installation including the lasr package. Windows users only need to select the R AddOn installation option during setup which installs a portable version of R including all necessary packages.
Installation of R AddOn under Unix/Linux
On Unix based systems R (version >= 3.3), several R packages and the lasr package needs to be installed to enable the tree based classification. Please make sure that the repositories version of R is 3.3 or newer by
or if already installed by typing
If your version is older than 3.3, please refer to the cran website on how to install the newest version of R on your system. Otherwise the standard installation step (e.g. on Ubuntu 18.04) can be performed
Furthermore, it is necessary to install some additional dependencies for subsequent commands (on all systems)
Next, install the following R packages that are required by the lasr package (takes several minutes to complete).
Make sure that all R packages were installed successfully. Pay attention to error messages and warnings similar to the following
| Warning in install.packages : installation of package [...] had non-zero exit status [...] |
since it indicates that a package installation failed. This may occur if some development packages/libraries are missing on your system. Finally, download and install the corresponding lasr package from the AddOns section.
To test if the lasr package was installed successfully, start R and load the package by the following commands:
Finally, install numpy that is required by the OPALS classify scripts (clfTreeModelTrain.py and clfTreeModelApply.py)
In case of problems please contact the OPALS developer team.
Extending the internal Python installation
OPALS comes with a fully functional Python interpreter. You may load OPALS modules as Python modules in an interactive Python shell, which can either be opened by double-clicking on $OPALS_ROOT/opals/python.exe, or in the Python IDE PyScripter by double-clicking on $OPALS_ROOT/addons/PyScripter/startPyScripter.bat. The next sections outline how to extend the internal Python installation with additional packages not contained in the OPALS distribution.
OPALS Python AddOns
Some Python packages have been found to complement OPALS especially well, namely the Python bindings for GDAL, NumPy, SciPy, and matplotlib. Under Windows simply select the Python AddOns option during setup. On Unix based systems the mentioned Python bindings must be installed manually using the Python package manager pip (also see below).
Kindly note that, if you want to use the Python bindings for GDAL using the internal Python installation, you must load the Python package opals or any OPALS module before gdal - otherwise, either no or the wrong GDAL DLL would be loaded.
Arbitrary Python Packages
If you want to use Python packages that are not contained in the OPALS Python AddOns, we recommend to use the PyPA recommended Python package manager pip. Python is shipped with the package ensurepip, which simplifies the installation of pip. Executing the following command in an OPALS shell:
installs pip, which can then be used to install the package of your choice, e.g. PyContracts:
searches for that package on the Python Package Index, downloads and installs it, including all requisite packages. Notice, however, that the installation may fail if the required package contains code written in a compiled language. In this case, you may search yourself for a binary installation package in the Wheel format, e.g. on C. Gohlke's website, download the appropriate archive, and supply its file path to pip in place of the package name:
If a binary installation package in the Wheel format is unavailable, you may instead find a legacy Windows installer (whose file name ends with .exe) for the respective package. Please mind in this case that, as mentioned in section Installing OPALS on Windows, installing OPALS does not affect the Windows registry (except of an uninstaller entry). This also means that the internal Python installation is not registered. However, legacy Windows installers for Python packages will search the Windows registry and let you choose only registered Python installations as the location where a package should be installed. Fortunately, those installers are also self-extracting archives, whose structure follow a common pattern, and hence, there exists a simple way how to use those installers for unregistered Python installations. To do so, you need to use a program that can inspect the contents of such archives. One such freely available program is 7-zip. Open the installer of the respective Python package with the archiver program of your choice, and extract the contained directory PLATLIB to $OPALS_ROOT/opals/Lib/site-packages/.
Configuring an external Python installation
If, for some reason, you decide to use a Python installation other than the one that comes with OPALS, there are two prerequisites:
- the platform (32/64 bit) of that Python installation must match the one of your OPALS installation.
- currently, OPALS can be used with Python versions 2.6, 2.7, 3.0, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, and 3.7
If these conditions are met, then you can re-configure OPALS to use an external Python installation by:
- deleting or renaming the following files:
$OPALS_ROOT/opals/python27.dll,$OPALS_ROOT/opals/python.exe, and$OPALS_ROOT/opals/pythonw.exe
- setting the environment variable
PYTHONHOMEto the root folder of the external Python installation - if using a Python version other than 2.7, then copy the contents of
$OPALS_ROOT/opals/python/x.y/(where x.y matches the version number of the Python installation to use) to$OPALS_ROOT/opals/, overwriting the existing files. - if using the Python package
gdal, then make sure to import the Python packageopalsor any OPALS module before importinggdal
In order to make the OPALS Python package accessible to the external Python installation (which allows for loading OPALS modules in the Python interpreter), there are two options:
- specification via the environment variable
PYTHONPATH:IfPYTHONPATHis undefined, then create it and set it to$OPALS_ROOT. IfPYTHONPATHalready exists, then prepend$OPALS_ROOTto it. - specification via
opals.pth:Create a text file namedopals.pthwithin the subdirectoryLib/site-packages/of your external Python installation. Open this text file in an editor, and insert the file path of your OPALS installation ($OPALS_ROOT), using the forward slash (/) as directory separator. As a reference, you may inspect$OPALS_ROOT/opals/Lib/site-packages/opals.pth.
If you don't have write access toLib/site-packages/within your external Python installation's directory, then you can createopals.pthin the directory%APPDATA%/Python/PythonXY/site-packages/(where "%APPDATA%" is an environment variable configured for your user account, and "XY" must be replaced by the version number of your external Python installation).
Note that your Python installation/IDE may clear PYTHONPATH upon startup, in which case the first option will fail. However, the second option should work in any case.
OPALS directory structure
This section describes the structure of an OPALS distribution. The main directory structure is as follows. If there are differences between Windows and Linux (e.g. opalsShell[.bat|.sh]) the Windows file is always specified first separated by a '|' character and followed by the Linux file:
directory: opals
The $OPALS_ROOT/opals/ directory contains the command line executables (*.exe|*.), the Python modules (*.pyd|*.so), and C++ shared libraries (opals*.dll|opals*.so) of all OPALS modules as well as a set of external shared libraries (e.g. gdal, xerces, mpfr...).
Furthermore, $OPALS_ROOT/opals/ contains a global python initialization file (__init__.py) responsible for loading all OPALS modules into the python environment.
Windows | Linux:
directory: cfg
The cfg directory contains the following files:
opals.cfg is the overall configuration file containing default values for a series of program parameters (options) common to all OPALS modules. opals.key is the key file containing licensing information. Please note, that the key file is not part of the OPALS distribution. In fact, if the opals.key file is missing, OPALS automatically runs in demo mode. OPALS supports a full featured demo mode, but the input is restricted to 1 Mio points. If you want to use OPALS for larger projects (in a commercial or educational environment), please contact the OPALS team for obtaining a license (Alternatively it is possible to put the opals.key file in the licence directory. See directory: licence for details).
directory: licence
From version 2.2.0 on it is possible to put the OPALS license file in a separate licence directory. This is beneficial when using OPALS as Docker container, since opals.key from the host system can be directly mounted into the container without changing the container itself. Please note, that first the cfg and then the licence directory is checked for the license file. If there is a license file in cfg, no further license tests will be performed. Hence, in case of an old or incorrect license file in cfg, a possibly correct license file in licence will be ignored. Details on the OPALS license and how to obtain one can be found here.
directory: packages
All OPALS package scripts (opalsPreprocess, opalsQuality, ...) are stored in the subdirectory python. These are python scripts providing standard workflows. A complete list of available OPALS packages can be found here.
directory:: c++_api
The contents are as follows:
Windows:
Each OPALS module is accessible as a C++ class via dynamic linkage. The corresponding (dynamic) link libraries are located in the lib subdirectory as separate module specific library files (on Windows: *.lib/*.dll). For including OPALS modules in custom C++ applications, the module interface header files (I<Module*>.hpp and the header files for custom (OPALS-specific) data types are required. These are located in the inc/opals subdirectory. Furthermore, the demo directory contains a demo source file (demo<Module*>.cpp) for each OPALS module demonstrating the use of the respective module in a C++ programming environment.
directory: demo
The OPALS distribution contains a number of test data along with some demo scripts. The test data also serve as basis for the examples given in the user manuals. To run the demo examples successfully, write permissions to this directory are required. If OPALS was installed to the default program folder, standard users do not have write access to these folders under Windows 7, 8, and 10. This is why (under Windows) the setup provides an installation option copying all demo files to an additional directory providing write access for all users. This directory if used as the startup directory of the corresponding OPALS Shell shortcut. If the "extra demo data" option wasn't selected during setup, you have three choices:
- Re-install opals and make sure the the extra demo data option is selected.
- Copy all demo files to a directory with write access (the OPALS setup does exactly the same) and run the demo examples there.
- start the opalsShell as administrator which gives you write permissions to all program folders.
OPALS installation check
As a final step, it is good practice to verify the integrity of the installation.
Execution on the command-line
For a quick check whether OPALS executables run properly, please start the OPALS shell, change to the directory $OPALS_ROOT/demo/, and submit the following commands:
After running these commands, the following files should exist:
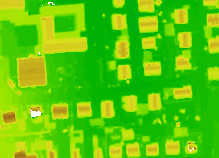
The derived DSM Z-Coloring should look like like this:
The pre-configured OPALS shell additionally offers aliases for the command line versions of the OPALS modules.
| Module name | Alias |
| opalsImport | Import |
| opalsExport | Export |
| opalsGrid | Grid |
| opalsCell | Cell |
| opalsZColor | ZColor |
| ... | ... |
Thus, the above commands can even be abbreviated and ...
... yields the same results as above (Note: whereas commands are case sensitive under Linux, commands under Windows are not. Hence, the capital letter(s) of the module names are mandatory under Linux only).
Python bindings
To check your configuration of Python, please open a OPALS shell and enter python. Within the Python interpreter, issue the following commands:
Please check, if the correct Python executable python.exe has been loaded, the correct Python DLL is in use, and the search directories include $OPALS_ROOT.
To check if the OPALS Python package can be loaded, open a Python shell and issue the following commands:
If the Python interpreter is able to load the OPALS Python module Import, then its absolute file path of the Import modue is printed, which should correspond to $OPALS_ROOT/opals/Import.pyd.
Platform specific restrictions
The following platform specific restrictions apply:
- MS windows
- no restrictions
- Linux
- The matlab based module (Module View, Module ICP and Module StripAdjust) do not finish correctly, if started within python
- PyScripter not available under Linux
- Python: Support for 2.7 versions only (2.6 and 3.x not supported yet)
- GDAL library is linked without: SCOP DTM, MrSID, ECW
