Derives shaded relief raster maps (geo-coded hill shading) of DEM grids.
Hill shading is a method to visualize a surface grid model by illuminating it using a light source shining from a certain direction. Artificial shadows are calculated depending on the slope (steepness) and exposition of the surface w.r.t the direction of the light source. Depending on the artificial shadow length, grey values (0=shaded..255=exposed) are assigned to each cell of the output raster.
To derive a shaded relief map an input grid model file is needed (parameter inFile). The resulting shaded image (parameter outFile) is stored as a regular grid in one of the Raster formats for visualization (parameter oFormat). The main calculation parameters are the position of the virtual light source (parameter sunPosition, azimuth and zenith angle) and the shading method. The following shading algorithms (parameter shading) are provided:
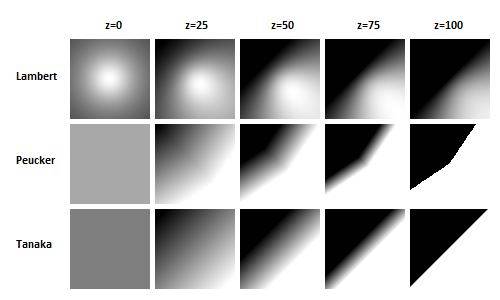
By default, the output grid is constructed according to the structure of the input grid (reference point, cell size, and number of columns and rows). However, a user defined output cell size can be defined (parameter pixelSize). User defined XY-limits (parameter limits) can either refer to the centers (=default) or corners of the outermost pixels (c.f. limit parameter description).
The slope values to be used for shading calculation must be estimated from the height values of the grid points. The estimated slope values are located in the center of 4 adjacent grid points. If XY-limits are not specified, then the estimated slope values will be used directly for the shading calculation, and therefore the resulting image is one column and one row smaller than the input grid. If parameters limits and/or pixelSize are specified, a bilinear resampling of the slope values will take place before the shading calculation.
Estimating slope values from heights can be avoided if corresponding grid features were derived with Module Grid. normalx/normaly or slope/exposition may be used alternatively as inputs using parameter feature. In this case, the resulting image will be the same size as the input grid if pixelSize is not specified.
Possible values: slope ........ steepest slope [%] (deprecated: use slpPerc instead) slpPerc ...... steepest slope [%] exposition ... slope aspect [rad] (deprecated: use expoRad instead) exposRad ..... slope aspect [rad] (azimuth of steepest slope) normalx ...... x-component of surface normal unit vector normaly ...... y-component of surface normal unit vector height ....... surface heightEither specify both normalx and normaly, both slope and exposition, or only height. The number of features must correspond to the number of inFiles
First we will use the following commands to generate a DSM from a subset of the ALS point cloud of strips G111, G112 and G113 using only a minimum set of parameters.
Now we can use Module Shade to compute hill shadings from this DSM using the following commands. We specify the input grid, the resulting raster image file, the shading algorithm, and the virtual sun position.
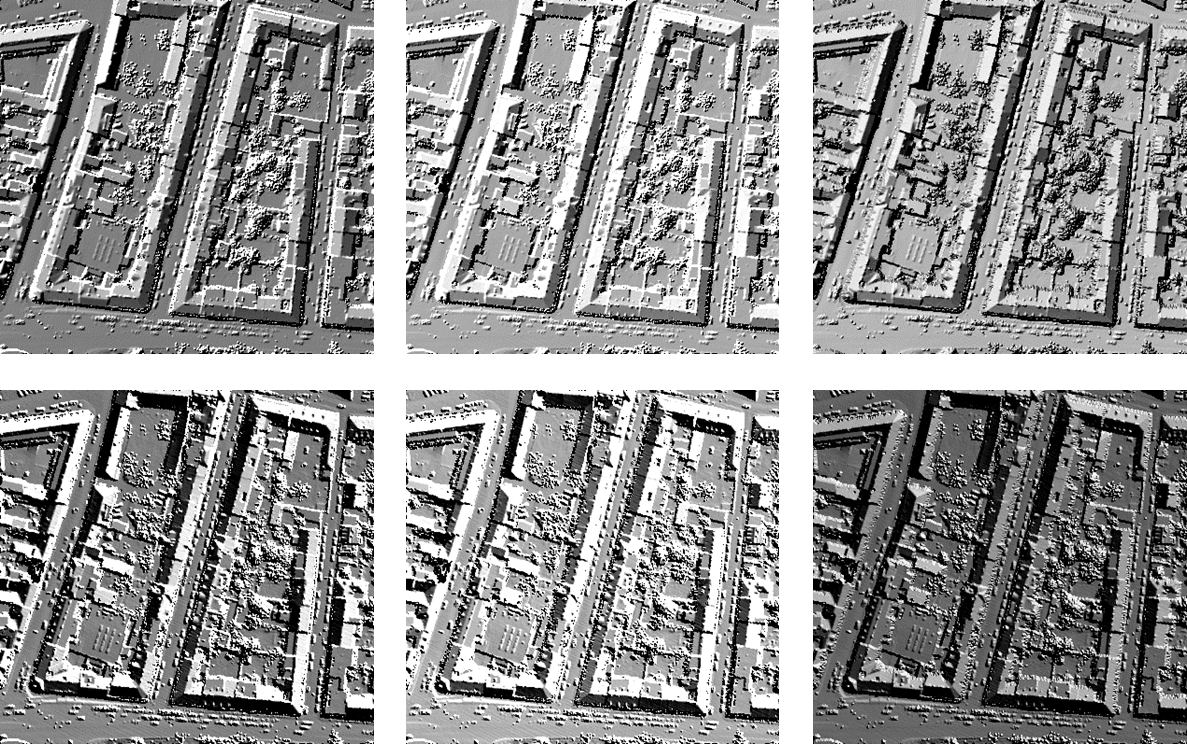
Alternately, we may use grid features normalx/normaly or slope/exposition as input.
Horn, B. K. P., "Hill Shading and the Reflectance Map," In: Proc. IEEE vol. 69, . 14–47, Jan 1981
Ecker, R., 1984, "Höhencodierung, Gefällsstufendarstellung und Schummerung aus einem DHM mit dem Optronics", Diplomarbeit, Institut für Photogrammetrie und Fernerkundung, TU Wien