OPALS supports reading and writing of Riegl DataBase (RDB) files (file extension is typically ".rdbx") with full attribute support using OPALS Format Definition (OFD) files. Conceptually RDB files are similar to ODM files since they can store arbitrary attributes and contain a spatial index based on primary coordinates. Whereas ODMs are limited to one arbitrary coordinate system, RDB supports multiple specific coordinate systems at the same time (although the spatial index is always based on to the primary coordinates).
Since RDB files are managed in a tangential cartesian coordinate system (Riegl call them project/application coordinate system), RDB files contain a 4x4 pose transformation matrix that allows direct conversion into ECEF (earth-centered, earth-fixed) coordinates. Furthermore, RDB files typically contain sensor coordinates as well, which is why, they can be used as direct input for Module StripAdjust as well.
The knowledge of those different coordinate system is relevant, because the user can control which coordinates should be imported or exported:
proj: project/application coordinate system (default)ecef: earth centered earth fixed coordinate system (requirement pose transformation matrix exists)scs: sensor coordinate system (import only; if available in the RDB file)map: map projection coordinates (import only; if available in the RDB file)From an OPALS point of view, points can be imported in proj, ecef and scs coordinate system. Furthermore, map coordinates can also be read if if stored in the RDB file. When exporting OPALS point clouds to RDB only two coordinate systems are reasonable: proj and ecef. If the OPALS point coordinates are given in ecef one must also specify the pose transformation matrix, allowing an implicit conversion to proj during export. This is done through the <pose> element in the OFD file, which takes either the matrix explcitely (matrix=) or alternavily takes the latitude, longitude and altitude of a certain point (point=) to compute the matrix.
When importing RDB files all attributes are read by default and where possible mapped to predefined opals Attributes. Custom attribtue selections for import (and export) can be created using a corresponding "OFD" file, similar as in the las/laz format. Note that attributes in RDB are not stored using a specific data type, but as integer values of different size. Floating-point values are converter to integer value based on the given scale, minValue and maxValue (for more details refer to Riegl rdblib documentation). This is why appropriate values for the aforementioned parameters are essential for storing attributes in RDB. When exporting RDB files those parameters can by either defined within the OFD file, or they are derived from the ODM statistic by Module Export. In other modules (e.g. Module Translate) the input attribute statistics might not be available. In this situation the definition of scale, minValue and maxValue is mandatory.
The following table contians all the XML-attributes which can be set for every <attribute> element in the OFD file:
| attribute | relevance | description | required? | default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | I/E | the OPALS attribute's name | YES | – |
| type | I/E | the OPALS data type (for a user-defined attributes) | NO; only for opals user-def attr. 1 | – |
| rdbName | I/E | the rdb attribute name; can contain index ([i]) for multi-dim Attributes | YES | name |
| rdbTitle | E | the rdb attribute title | NO; only for non-predef rdb attr. 2 | <empty> |
| rdbDescription | E | textual description of the rdb attribute | NO; only for non-predef rdb attr. 2 | <empty> |
| unit | E | the physical rdb unit symbol, like "m", "rad", "K", etc. | NO; only for non-predef rdb attr. 2 | <empty> |
| scale | E | the scale/resolution to select the appropriate rdb storage size | NO; only for non-predef rdb attr. 2; derivable from ODM 3 | <see text> |
| minValue | E | the theoretical minimum value to select the appropriate rdb storage size | NO; only for non-predef rdb attr. 2; derivable from ODM 3 | <see text> |
| maxValue | E | the theoretical maximum value to select the appropriate rdb storage size | NO; only for non-predef rdb attr. 2; derivable from ODM 3 | <see text> |
| defaultValue | E | the default value (minimum <= default <= maximum) | NO; only for non-predef rdb attr. 2 | <see text> |
| invalidValue | E | the invalid value (minimum <= invalid <= maximum; use "not-a-number" if there is no invalid value) | NO; only for non-predefined rdb attr. 1 | <see text> |
| toOpals | I | the conversion formula from rdb to OPALS attribute (e.g. "x*pi/180") | NO; somtimes adviced for conv. 4 | <empty> |
| toRdb | E | the conversion formula from OPALS to rdb attribute (e.g. "x/pi*180") | NO; somtimes adviced for conv. 4 | <empty> |
In the simplest case (predefined rdb and opals attributes) name and rdbName are enough to fully define an attribute for import/export. All other XML-attributes are only required in some of the following cases:
1: only required to export opals user-defined attributes2: only required for export of non-predefined rdb attributes3: can in some cases be derived from ODM satistics if not provided4: never mandatory but strongly advided for conversion of certain attibutes (e.g. angles are stored ad rad in opals and as deg in rdblib)To identify invalid attribute values (=nodata) RDB uses an invalidValue similar as the nodata value for raster file. This optional number must also lie within the defined minValue and maxValue. In case no invalid value should be used, set invalidValue to nan (not-a-number).
For the export of predefined RDB attributes (starting with "riegl.") the rdbName is enough as all other information about the attribute (rdbTitle, rdbDescription, unit, scale, minValue, maxValue, defaultValue, invalidValue) is already set with a fixed value within rdblib and cannot be overwritten! Doing so, doesn't have any effect, since the predefined values are used instead.
For completeness it is mentioned that min, max and scale parameters have to be set for coordinates as well. But there only one parameter set is used for all coordinate axes. Hence, x, y and z of all points needs to fit between min and max. As for the attributes, the OPALS modules use the coordinate bounding box of input data to set appropriate parameters. If not available the definition within the OFD file is mandatory. This is done through the min, mac and scale attributes of the optional <primaryAttribute> xml element.
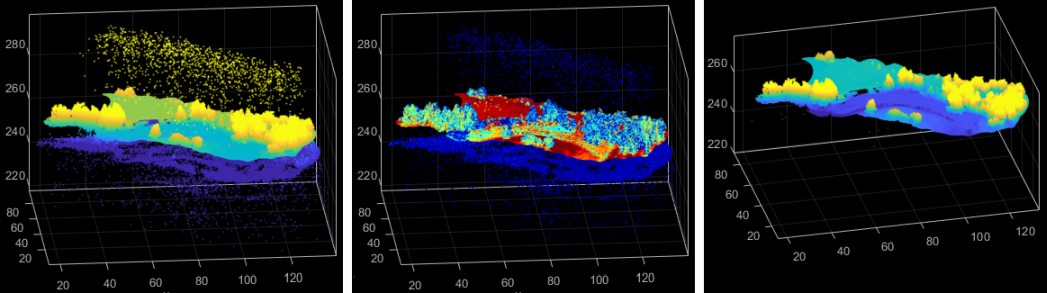
The follow example imports an rdbx file with defined attributes and sensor coordinates into an ODM. Then, the ODM is exported back into an rdbx file filtering low amplitude echos (lower than -35db) to eliminate most outliers. The use OFD file can be found in the demo directory and is listed below:
Figure 1 shows different 3d views of the demo data set. As visible on the left the raw point cloud contains a significant amount of noisy echoes. Coloring the point cloud by amplitude values, reveals a low amplitude for most outliers. Applying an appropriate amplitude filter (see above) a cleaned point cloud can be achieved, as shown on the right.